Lighting: Getting started
Types of lights
Led Panel Lights
Led spotlights
Soft lighting effect
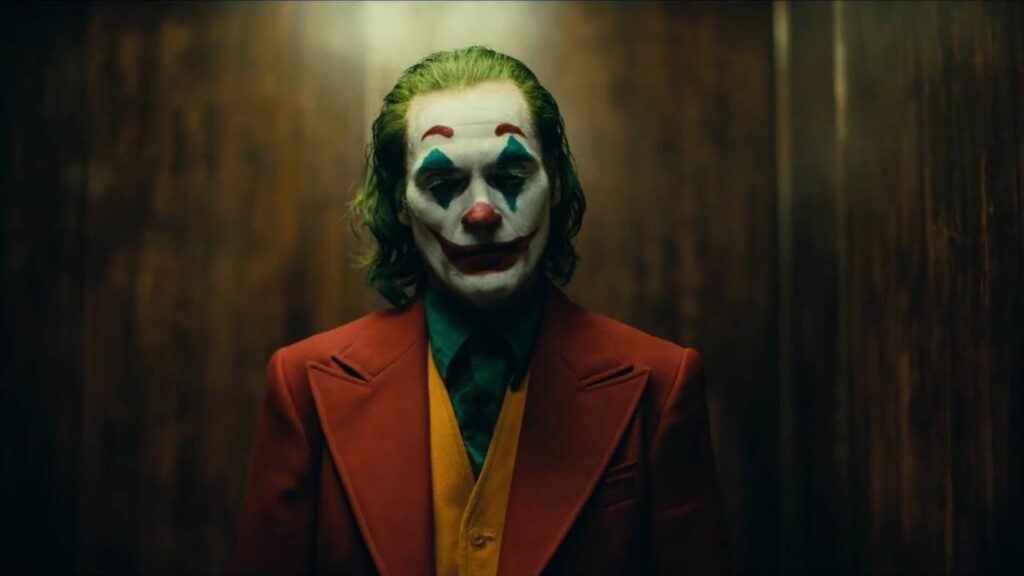

Harsh lighting effect

Black light
Black light effect with coloured panels…. avoid the glow?
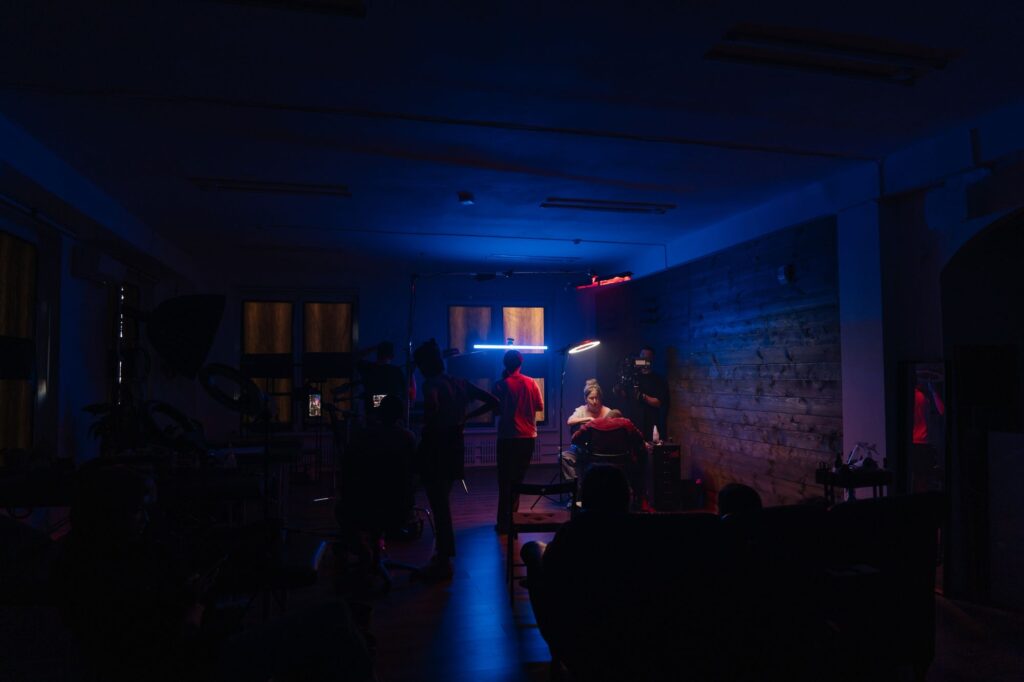


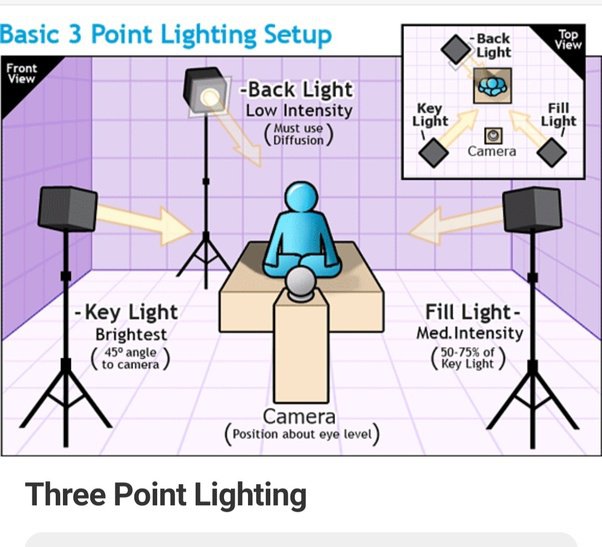
Three point lighting system
Colour grading
We will revisit this in a later week during post production!
Lighting for greenscreen
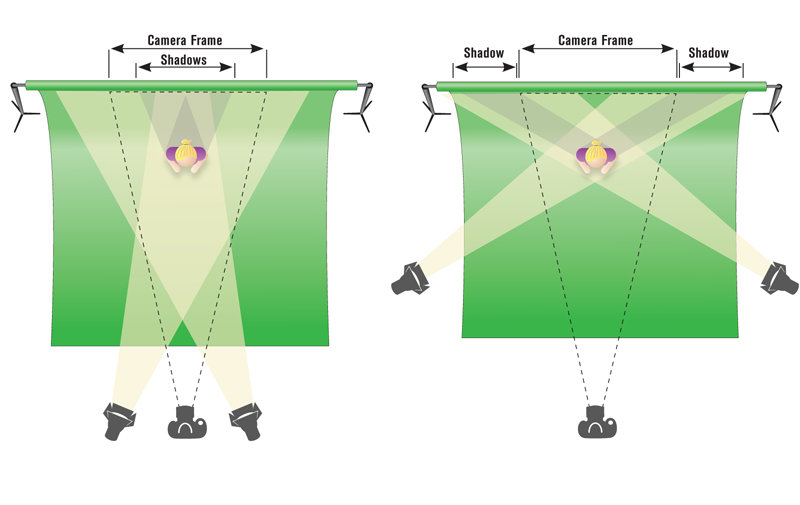
- The use of digital cameras. When using a digital camera instead of film, you obtain better results from a green screen shoot because of the cleanness and luminescence of green over blue. Using green instead of blue results in less noise when keying out the footage.
- Color spill. While the green or blue screens will be removed during editing, some color will “spill” onto the subjects, especially around the edges. This can create a thin line around the person, or make areas like their hairline look odd. Depending on your shoot, color spill can be better or worse depending on the color of your screen. Blue screen tends to have less spill than green, and also happens to be easier to color correct than green.
- The prevalence of blue. Subjects and objects are more likely to be blue than green. For example, people are more likely to be wearing blue clothing than green clothing. You get better results when the background color is not heavily present in the subject you are filming (which is why red screens and yellow screens don’t exist).
- Lighting. Blue screens have a lower luminosity as compared to green screens. This means they are better suited to low-light shoots, but also makes them trickier to light. If you want the blue screen to key properly with the least amount of adjustments necessary you’ll need to set your camera to a higher f-stop than you would were you using a green screen. This also means it is more difficult to shoot a large scene on blue screen as opposed to green.
Why not to shade with black in post
Shading with hue instead of black